LinkedIn Sales Navigator is a robust platform tailored for sales professionals to manage and streamline their lead generation processes. With its array of advanced tools, Sales Navigator enhances your ability to pinpoint and engage with decision-makers, monitor their professional activities, and stay updated on industry movements. This guide will provide a comprehensive, step-by-step walkthrough for using LinkedIn Sales Navigator to navigate and build targeted lead lists without any mention of external scraping or outreach tactics.
Before exploring the core functionalities, it’s essential to set up your Sales Navigator environment effectively.
Steps:
Accessing Sales Navigator: Once logged in to LinkedIn, select "Sales Navigator" from the LinkedIn Premium menu, which will direct you to the Sales Navigator dashboard.
Customizing Your Dashboard: Take a moment to adjust the dashboard settings by indicating industries, regions, or job functions you’re most interested in. These settings tailor your experience, showing insights and updates that are relevant to your prospecting goals.
Sales Navigator’s powerful search and filter functions allow you to pinpoint potential leads with precision. Here, we'll walk through each step and feature in detail.
Using Advanced Filters in Sales Navigator
Sales Navigator provides an extensive selection of search filters to narrow down your audience, offering more than 30 options that cover a range of categories. Each filter is built to optimize your ability to target the right audience with maximum relevance.
Filter Categories and How to Use Them:
Company Filters
Industry: Choose industries relevant to your business. For instance, if you’re targeting the technology sector, you can select “Computer Software” or “Information Technology.”
Company Size: Filter companies by employee count to target enterprises of a specific scale. Options range from small businesses to large enterprises (e.g., “51-200 employees” or “10,000+ employees”).
Headcount Growth: Focus on companies experiencing growth by selecting recent headcount increases, which can indicate expansion and potential needs for new services.
Role Filters
Job Title: Input specific titles (e.g., “Head of Sales,” “Marketing Director”) to target individuals in these roles.
Seniority Level: Filter leads based on seniority levels like “Manager,” “Director,” or “Executive.” This allows you to prioritize key decision-makers.
Personal Filters
Location: Specify a geographic region to limit your search results to certain cities, states, or countries.
Years of Experience: Adjust results based on the number of years in a role or industry, helpful when looking for seasoned professionals.
Dynamic Filters (e.g., Recent Updates)
Job Change Alerts: Identify leads who recently changed roles, as new positions may signal openness to exploring new solutions.
Posted Content: Find prospects who are actively posting or engaging with content on LinkedIn, which may indicate engagement with relevant topics in your industry.
How to Set Up an Advanced Filter Search in Sales Navigator
Steps:
Open the Sales Navigator Search Interface: From the main dashboard, select “Advanced Search.”
Choose Your Filters: Begin by selecting the most critical filters for your search criteria. For example, if targeting technology directors in the software industry within a certain location, set filters for Industry, Job Title, Location, and Seniority.
Preview and Refine: As you apply filters, the results will adjust in real time. Review these initial results to ensure they align with your target profile. Adjust filters if the results are too broad or narrow.
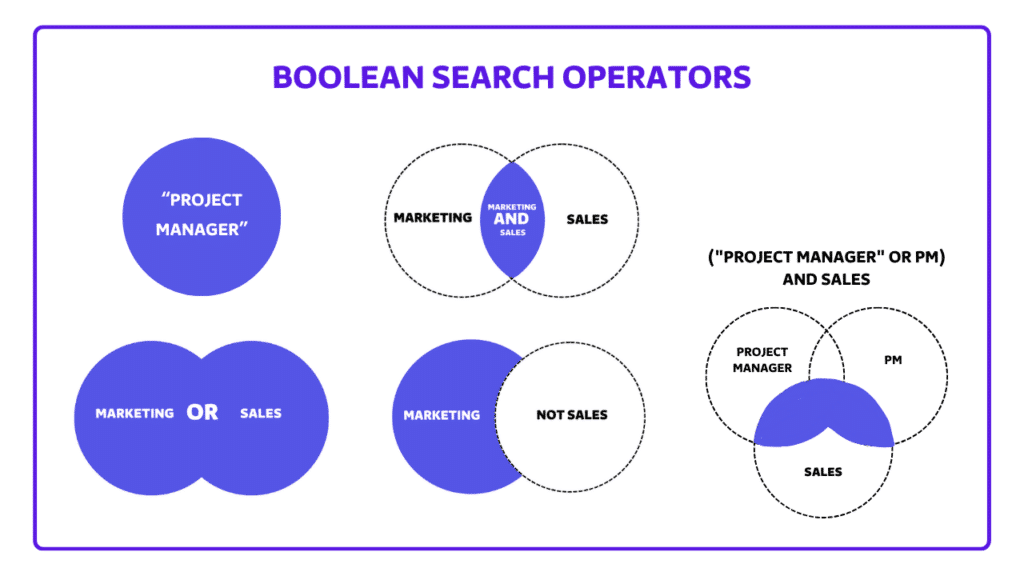
Using Boolean Search for Enhanced Precision
Sales Navigator’s Boolean search lets you refine searches using logic-based commands. This feature is invaluable when narrowing down a specific profile type or excluding irrelevant profiles.
Common Boolean Operators:
AND: Combines terms, ensuring that results include all specified terms.
Example: Searching “Marketing AND Manager” will display profiles containing both terms.
OR: Shows profiles that contain at least one of the specified terms.
Example: “Sales OR Business Development” includes profiles with either term.
NOT: Excludes specific terms from results.
Example: “Marketing NOT Assistant” will exclude profiles containing “Assistant.”
Parentheses and Quotes: Parentheses organize complex search criteria, and quotes specify exact phrases.
Example: (VP OR “Vice-President”) AND (“Sales” OR “Marketing”) NOT “Assistant”
How to Construct a Boolean Search in Sales Navigator
Steps:
Access the Search Bar: Open Sales Navigator’s search interface.
Input Your Boolean Query: Enter your desired search string, applying parentheses to group keywords and using quotes for specific titles or phrases.
Verify and Adjust Results: Check the results to confirm that the Boolean logic is working as expected. Refine the query if needed to achieve more targeted results.
To maximize the effectiveness of Sales Navigator, it’s essential to go beyond basic search and list-building techniques. Here are some advanced tips and best practices that can improve the quality of your results and reduce time spent filtering out unqualified leads.
Using Filters Wisely to Optimize Searches
Sales Navigator’s filter system is robust, but improper use of filters can still yield irrelevant results. Here’s how to get the best results from key filters.
Tips for Key Filters:
Keyword Filter Caution: When using the keyword filter, remember it searches the entire profile, not just job titles or experience. For instance, searching “Marketing” could yield anyone with a mention of “Marketing” anywhere in their profile.
Best Practice: Limit keywords to niche terms likely to appear in job descriptions but not in broader contexts, like “Offline Marketing” or “Event Sponsorship.”
Job Title vs. Keyword Filter: When looking for specific job roles, the Job Title filter is typically more accurate than the Keyword filter, as it specifically targets current positions rather than any mention within the profile.
Example: Use “Head of Marketing” in the Job Title filter instead of “Marketing” in the Keyword filter.
Exclude Irrelevant Results with the NOT Operator: Use Boolean logic (NOT) in the Keyword filter to exclude roles or terms that might appear alongside your target job title but indicate an irrelevant profile.
Example: Searching for “Marketing NOT Assistant” excludes profiles with “Assistant” titles.
Avoiding Overuse of Seniority and Function Filters
Sales Navigator’s Seniority and Function filters attempt to classify profiles based on job roles and hierarchies, but these filters can sometimes misinterpret job titles. Here’s how to use them effectively—or avoid them if unnecessary.
Best Practices:
Use When Exploring New Titles Only: The Seniority filter can be helpful if you’re exploring a broad category of professionals, like all decision-makers in “Sales.” Otherwise, it can misclassify roles, causing you to miss relevant profiles.
Skip if You Know Target Titles: If you already know the job titles you’re interested in, use the Job Title filter instead. This ensures you target specific profiles without the risk of misclassification.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls with Industry and Technology Filters
Some filters, like Industry and Technology, may not always yield accurate results due to LinkedIn’s classification process. Here’s how to use these filters wisely.
Industry Filter Tips: Rather than relying on the Industry filter alone, combine it with company size or headcount growth filters for more accurate results.
Technology Filter Alternatives: LinkedIn’s technology filters aren’t always precise. For more reliable results, consider external tools for identifying companies based on technology use if this is a priority for your list.